What is a Solenoid Valve?
A solenoid valve is an
electromechanical device used for controlling liquid or gas flow. The
solenid valve is controlled by electrical current, which is run through a
coil. When the coil is energized, a magnetic field is created, causing a
plunger inside the coil to move. Depending on the design of the valve,
the plunger will either open  or close the valve. When electrical current is removed from the coil, the valve will return to its de-energized state.
or close the valve. When electrical current is removed from the coil, the valve will return to its de-energized state.
 or close the valve. When electrical current is removed from the coil, the valve will return to its de-energized state.
or close the valve. When electrical current is removed from the coil, the valve will return to its de-energized state.
In direct-acting solenoid valves, the plunger directly opens
and closes an orifice inside the valve. In pilot-operated valves (also
called the servo-type), the plunger opens and closes a pilot orifice.
The inletline pressure, which is led through the pilot orifice, opens
and closes the valve seal.
The most common solenoid valve has two ports: an inlet port and
an outlet port. Advanced desigs may have three or more ports. Some
designs utilize a manifold-type design.
Solenoid valves make automation of fluid and gas control
possible. Modern solenoid valves offer fast operation, high
reliability, long service life, and compact design.
Please visit our Solenoid Valve Basics page for more detailed information on solenoid valve operation..
What are the different parts of a solenoid valve?
The illustration below depicts the basic components of a solenoid valve. The valve shown in the picture is a normally-closed, direct-acting valve. This type of solenoid valve has the most simple and easy to understand principle of operation.
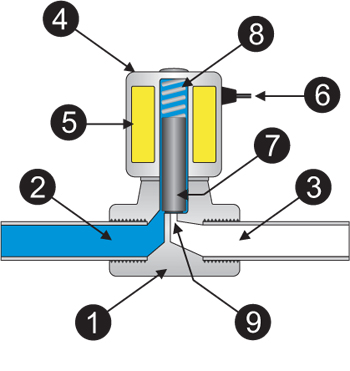
1. Valve Body
|
4. Coil / Solenoid
|
7. Plunger
|
2. Inlet Port
|
5. Coil Windings
|
8. Spring
|
3. Outlet Port
|
6. Lead Wires
|
9. Orifice
|
How does a solenoid valve work?
The media controlled by the solenoid valve enters the valve through the inlet port (Part 2 in the illustration above). The media must flow through the orifice (9) before continuing into the outlet port (3). The orifice is closed and opened by the plunger (7).
The
valve pictured above is a normally-closed solenoid valve.
Normally-closed valves use a spring (8) which presses the plunger tip
against the opening of the orifice. The sealing material at the tip of
the plunger keeps the media from entering the orifice, until the plunger
is lifted up by an electromagnetic field created by the coil.
The video animation below shows the operation sequence for a direct-acting solenoid valve.
God bless us all.....:)